1.2.2 Network Topologies and Descriptions
Networks vary in size depending on the networking requirement. A technician must be knowledgeable about the different types of networks available to connect end devices and corporate sites.
PAN
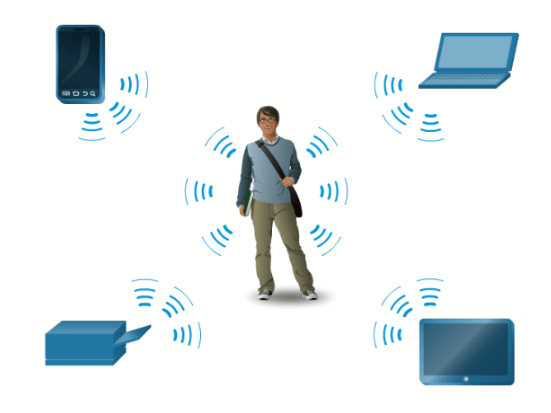
A personal area network (PAN) is a network that connects devices, such as mice, keyboards, printers, smartphones, and tablets within the range of an individual person. These devices are most often connected with Bluetooth technology. Bluetooth is a wireless technology that enables devices to communicate over short distances.
LAN
Traditionally, a local area network (LAN) is defined as a network that connects devices using wire cables in a small geographical area. However, the distinguishing characteristic for LANs today is that they are typically owned by an individual, such as in a home or small business, or wholly managed by an IT department, such as in a school or corporation.
VLAN
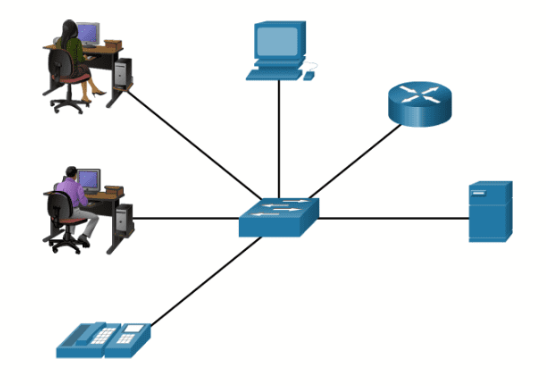
Virtual LANs (VLANs) allow an administrator to segment the ports on a single switch as if it were multiple switches. This provides more efficient forwarding of data by isolating traffic to only those ports where it is required. VLANs also allow end devices to be grouped together for administrative purposes. In the diagram, VLAN 2 creates a virtual LAN for IT’s computers, even on different floors, and can have different network permissions set than the other VLANs.
WLAN
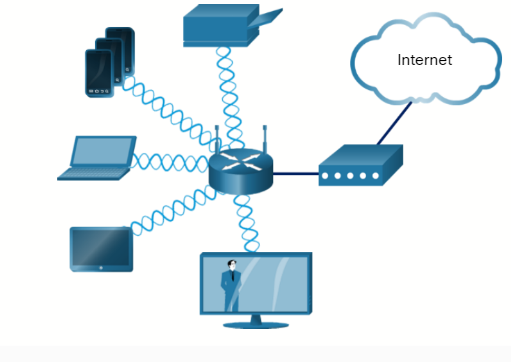
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is similar to a LAN but wirelessly connects users and devices in a small geographical area instead of using a wired connection. A WLAN uses radio waves to transmit data between wireless devices.
WMN
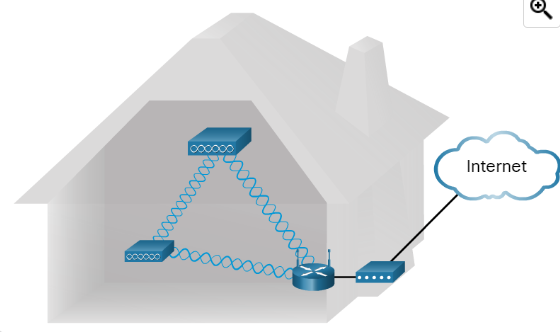
A wireless mesh network (WMN) uses multiple access points to extend the WLAN. The topology shows a wireless router. The two wireless APs extend the reach of the WLAN within the home. Similarly, businesses and municipalities can use WMNs to quickly add new areas of coverage.
CAN
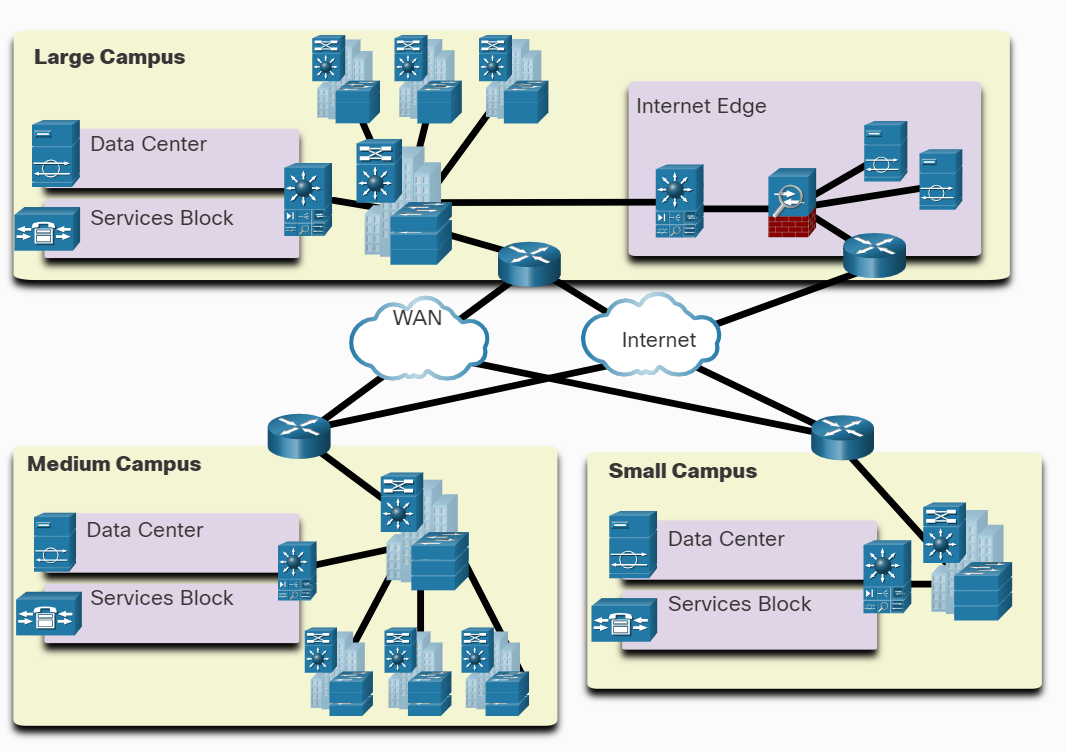
A campus area network (CAN) is a group of interconnected LANs, belonging to the same organization and operating in a limited geographical area. These can be both academic campuses and business or corporate campuses. Campus area networks typically consist of several buildings interconnected by high-speed Ethernet links using fiber optic cabling. The figure shows three different sized campus area networks.
MAN
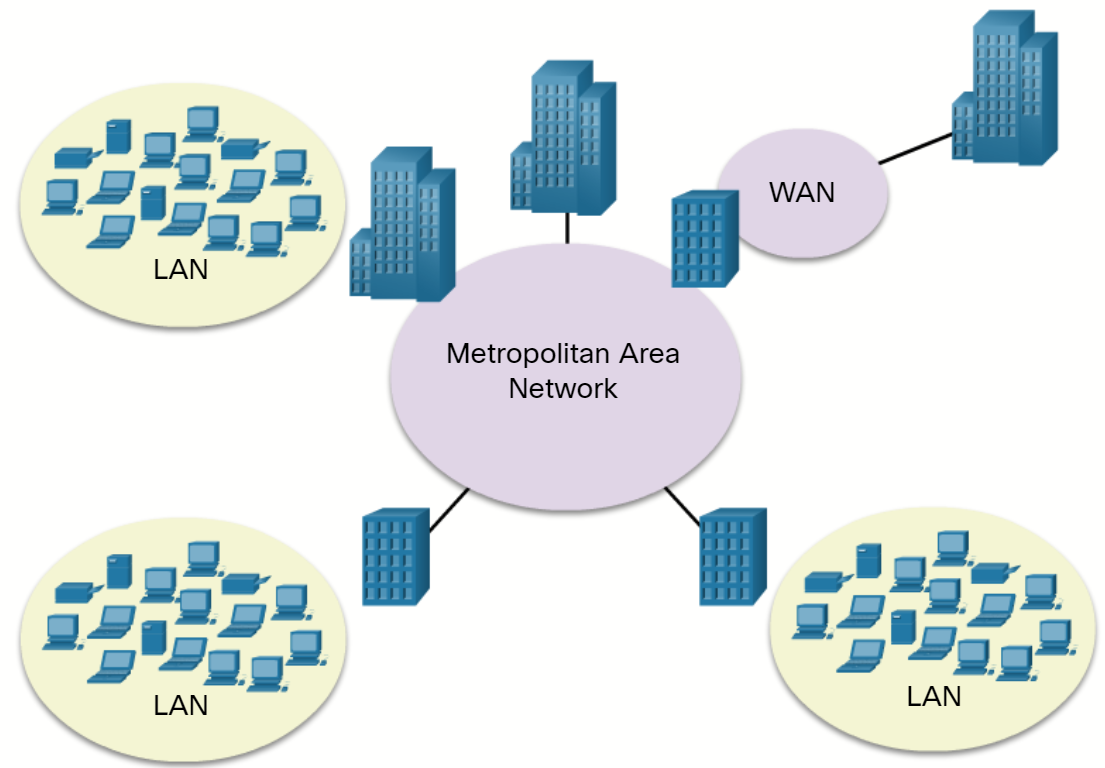
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that spans across a large campus or a city. The network consists of various buildings connected through wireless or fiber optic media.
WAN
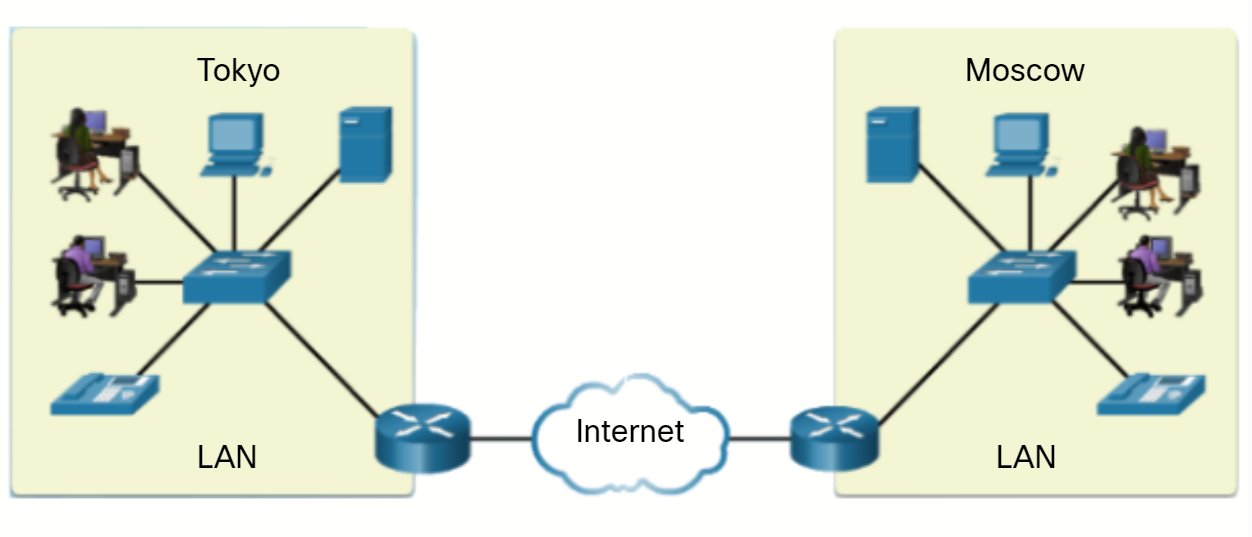
A wide area network (WAN) connects multiple networks that are in geographically separated locations. Individuals and organizations contract for WAN access from a service provider. Your service provider for your home or mobile device connects you to the largest WAN, the internet. In the figure, the Tokyo and Moscow networks are connected through the internet.
VPN
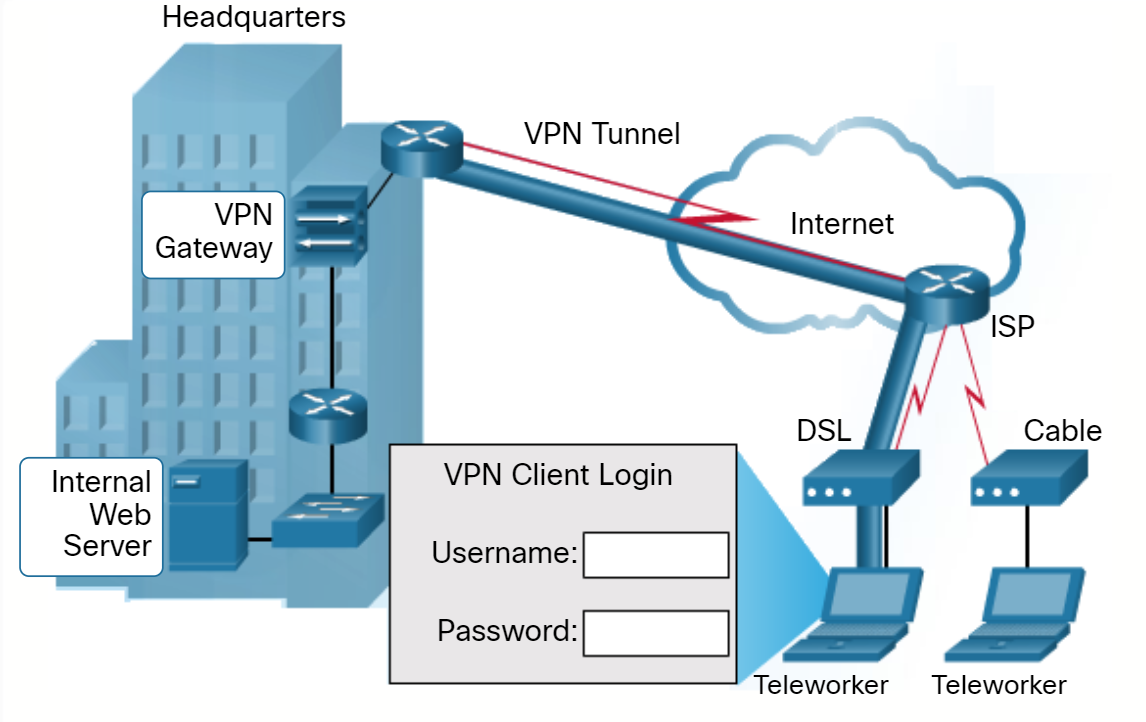
A virtual private network (VPN) is used to securely connect to another network over an insecure network, such as the internet. The most common type of VPN is used by teleworkers to access a corporate private network. Teleworkers are network users that are offsite or remote. In the figure, the fat links between Teleworker 1 and the router at the Company Headquarters represent a VPN connectio